Introduction
Have you ever heard the term “high cholesterol“? It’s a common condition, but the medical term for it is hyperlipidemia. This simply means you have high levels of fats, called lipids, circulating in your bloodstream.
While it often doesn’t cause any immediate symptoms, hyperlipidemia can be a serious health concern if left untreated.
This article looks closely at understanding hyperlipidemia, exploring its causes, potential symptoms, diagnosis methods, and various treatment options.
We’ll also discuss how to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle to manage hyperlipidemia and reduce your risk of complications.
What is Hyperlipidemia?
Our blood contains various components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and lipids. Lipids are essential fats that play a vital role in our body’s functions.
However, when there’s an imbalance in these fats, particularly high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides, it can lead to hyperlipidemia.
Surprisingly, more than 1.5 million cases of hyperlipidemia occur in Nigeria yearly.
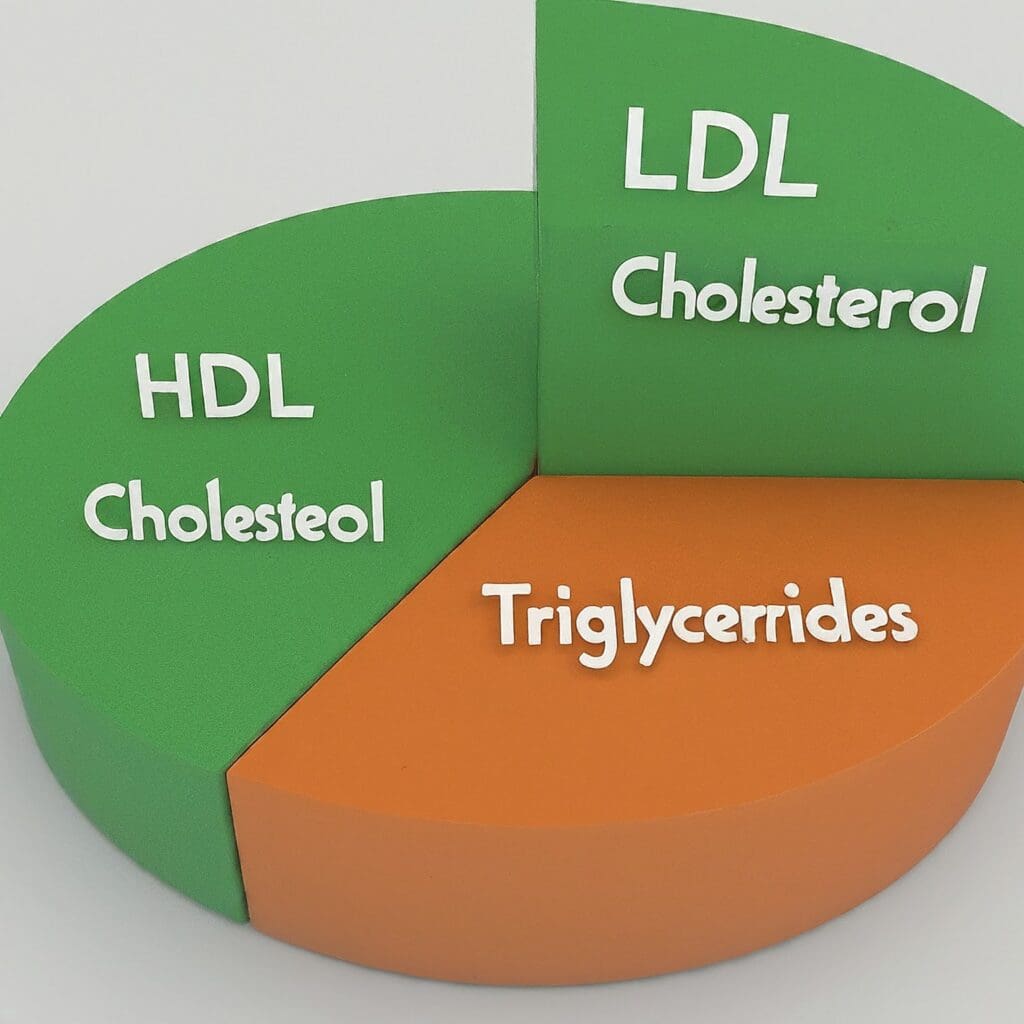
There are different types of cholesterol:
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, LDL transports cholesterol to your cells. When there’s too much LDL, it can build up in your arteries, forming plaque. This plaque narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Considered “good” cholesterol, HDL removes excess cholesterol from your arteries and carries it back to your liver for disposal. Having healthy HDL levels helps prevent plaque buildup.
- Triglycerides: Another type of fat in your blood, triglycerides come from the calories you consume. High triglyceride levels, along with high LDL, further contribute to plaque formation.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia
Several factors can contribute to hyperlipidemia. Some are controllable, while others are not:
- Diet: A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and added sugars can increase LDL and triglycerides.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can elevate LDL and triglycerides while lowering HDL.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise reduces HDL levels.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessel walls and increases LDL levels.
- Family History: Having a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease increases your risk.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can raise your risk.
- Medications: Some medications might elevate your cholesterol or triglycerides as a side effect.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
The tricky part about hyperlipidemia is that it often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This is why it’s crucial to get regular checkups and blood tests to identify it before complications arise.
In some advanced cases, people with hyperlipidemia might experience:
- Chest pain (angina): This can occur with exertion or even at rest.
- Pain in the legs or feet: Especially in the calves, this pain can be caused by narrowed arteries reducing blood flow.
- Shortness of breath: This can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Signs of a stroke or heart attack: These are emergencies and require immediate medical attention.
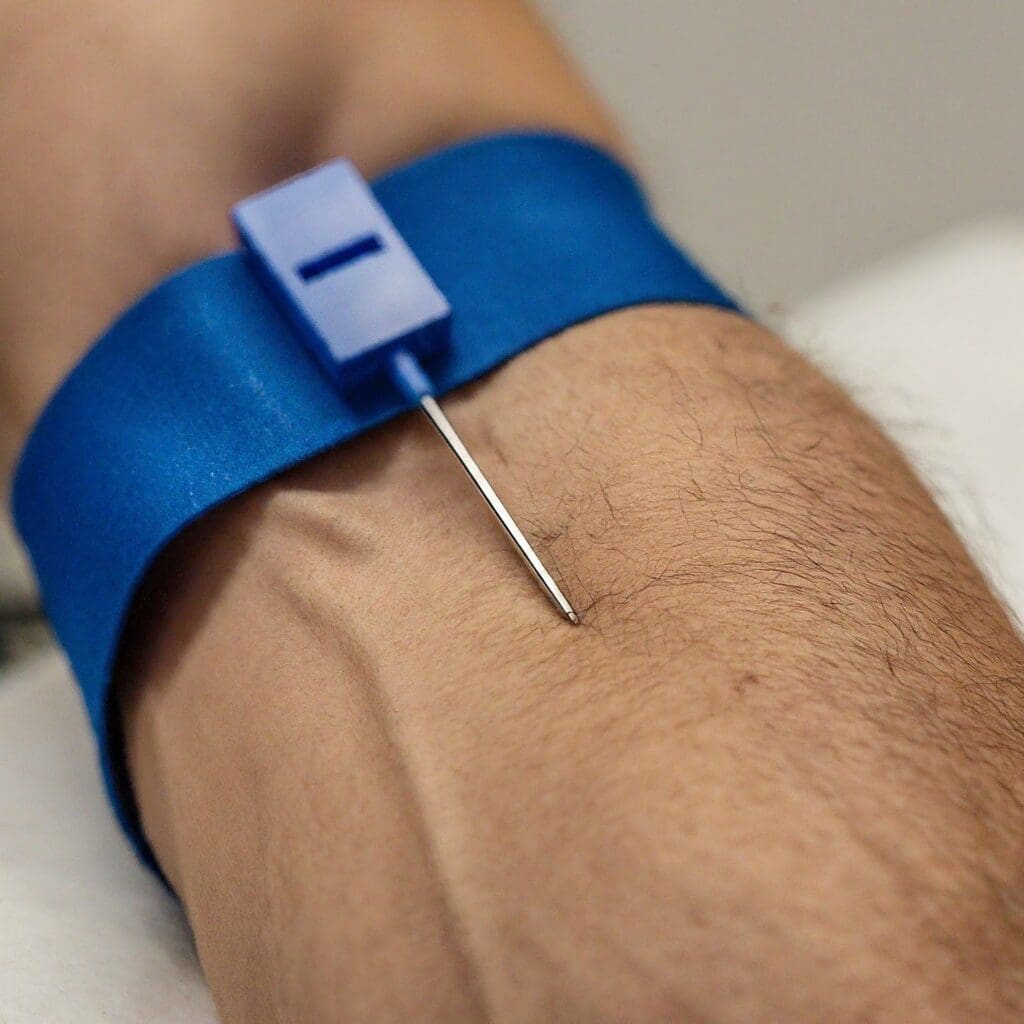
Diagnosing Hyperlipidemia
The primary method for diagnosing hyperlipidemia is a simple blood test called a lipid panel or lipid profile. This test measures your levels of:
- Total Cholesterol
- LDL Cholesterol
- HDL Cholesterol
- Triglycerides
Based on these levels, your doctor will determine your risk of heart disease and create a treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Hyperlipidemia
The good news is that hyperlipidemia is a manageable condition. Treatment usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications, depending on the severity of your case.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: A heart-healthy diet is crucial. Focus on:
- Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: These are rich in fiber, which helps lower LDL.
- Lean protein sources: Opt for fish, poultry, and legumes.
- Healthy fats: Include unsaturated fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Limit saturated and trans fats: These are found in red meat, processed foods, and fried foods.
- Reduce added sugar and refined carbohydrates: These can contribute to high triglycerides.
- Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing weight can improve cholesterol levels
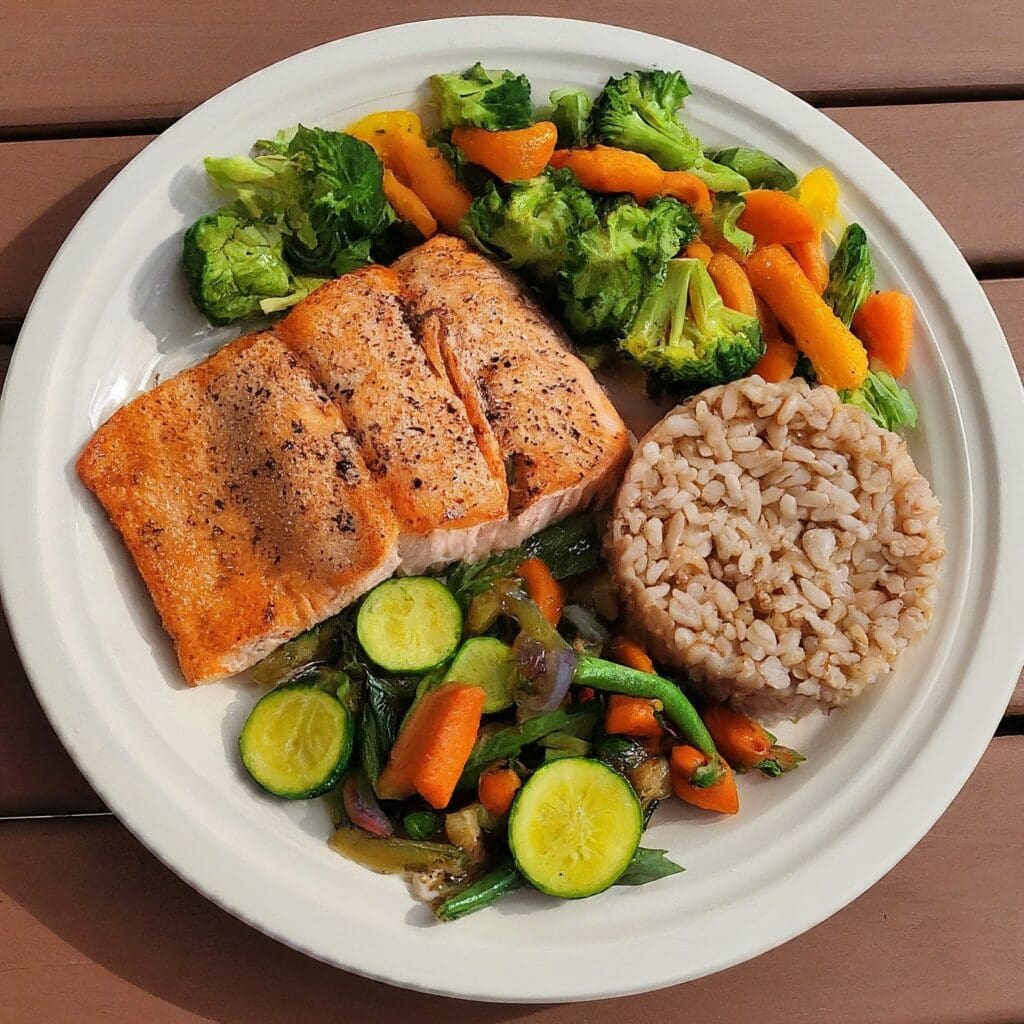
Medications:
If lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough to manage your cholesterol levels, your doctor might prescribe medications. Here are some common types:
- Statins: These are the first-line medication for lowering LDL cholesterol. They work by blocking the liver’s production of cholesterol.
- Ezetimibe: This medication helps reduce cholesterol absorption in your gut.
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: These medications bind to bile acids in your digestive system, forcing your liver to use more cholesterol to produce new bile acids, thereby lowering LDL levels.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: This is a newer class of injectable medications that target a specific protein that regulates LDL levels.
Monitoring and Follow-up:
Once you start treatment for hyperlipidemia, it’s crucial to monitor your progress with regular blood tests. Your doctor will adjust your treatment plan as needed to ensure you reach your target cholesterol levels.
Living a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Here are some additional tips for living a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing hyperlipidemia:
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to unhealthy lifestyle choices and raise blood pressure. Try relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can increase triglycerides.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- See your doctor regularly: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
Preventing Hyperlipidemia
The good news is that many of the strategies for managing hyperlipidemia can also help prevent it from developing in the first place. Here are some preventive measures:
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet from a young age.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Don’t smoke.
- Know your family history and talk to your doctor about your risk factors.
Conclusion
Hyperlipidemia, often referred to as high cholesterol, is a common condition that can significantly increase your risk of heart disease if left untreated. The good news is that it’s a manageable condition with a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. By following a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can lower your cholesterol levels, reduce your risk of complications, and live a long and healthy life.
Remember: This article provides general information and shouldn’t be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment specific to your situation.



